An Introduction to the World of Machine Learning: From Buzzword to Breakthrough
Table of contents
- Understanding the Fundamentals
- Brief History of Machine Learning
- Why Machine Learning Became the Hottest Buzzword in Tech
- The Incredible Impact of Machine Learning Across Various Sectors
- A Look at the Different Types of Machine Learning Algorithms
- Creating Your First Machine Learning Model Using the IRIS Dataset
- Conclusion
Machine learning (ML) has become one of the hottest buzzwords in the tech industry in recent years. It has transformed the way we think about data analysis and decision-making, leading to incredible breakthroughs in a wide range of sectors. In this blog, we will explore the world of ML, its brief history, the reasons behind its popularity, and the impact it has had on various sectors. We will also take a closer look at the different types of machine learning algorithms and walk through a step-by-step guide to creating your first ML model using the popular IRIS dataset.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Imagine you are trying to teach a robot how to identify different types of fruits. You could try to program the robot to recognize each fruit by writing code for each individual fruit. However, this would be time-consuming and impractical if you had a large number of different fruits to identify.
Instead, you could use machine learning to train the robot to recognize fruits on its own. You would start by showing the robot a set of labelled examples of different fruits, such as apples, oranges, and bananas. The robot would analyze these examples and try to identify patterns and characteristics that distinguish one fruit from another. For example, it might learn that apples are generally round and red or green, while bananas are elongated and yellow.
Once the robot has learned to recognize these different fruit types, you can test its ability to identify new examples that it hasn't seen before. For example, you could show it a picture of a pear, and the robot would use its machine learning model to predict that it is a type of fruit.
Thus, machine learning can be described as a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on the development of algorithms and models that can learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. ML is a powerful tool that is becoming increasingly important in various industries such as healthcare, finance, marketing, and transportation, among others.
This provides machines the capability to think in the same manner as humans do. A machine, with aid of machine learning, can complete almost any task which is given to it by just automating it with the data-defined trends and a set of given rules. The importance of ML lies in its ability to extract meaningful insights from large and complex datasets that would be impossible for humans to process manually. Machine learning has a collection of algorithms that are designed to learn and derive insights from an enormous cluster of data independently without being explicitly programmed to do so. These algorithms, with time, improve their accuracy in predicting the outcome independently without any human intervention. This can help businesses make data-driven decisions, improve their products or services, and ultimately, increase their revenue and profitability.
Brief History of Machine Learning
The roots of machine learning (ML) can be traced back to the mid-20th century when researchers began exploring the concept of artificial intelligence (AI). The term "machine learning" was coined by Arthur Samuel in 1959, who defined it as the ability of computers to learn without being explicitly programmed.
In the 1960s and 1970s, researchers began developing algorithms for machine learning, including linear regression and decision trees. However, the lack of computing power and data made it difficult to apply these algorithms to real-world problems.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the development of more powerful computers and the availability of larger datasets led to a resurgence of interest in machine learning. Neural networks, which had been developed in the 1950s, were improved and used for applications such as handwriting recognition and speech recognition.
In the early 2000s, the availability of large-scale data and the development of new algorithms such as support vector machines (SVMs) and random forests led to significant advances in machine learning. These advances enabled the development of applications such as recommendation systems and image recognition.
In the past decade, the development of deep learning techniques, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), has revolutionized the field of machine learning. These techniques have achieved state-of-the-art performance on a wide range of tasks, including image classification, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
Why Machine Learning Became the Hottest Buzzword in Tech
There are several reasons why machine learning (ML) has gained popularity in the past few years:
Availability of Data: The widespread use of the internet and social media has led to exponential growth in the amount of data that has been created, copied, captured, and circulated worldwide. This data can be used to train machine learning models to make predictions and provide insights. According to reports, data is expected to grow up to 180 Zeta bytes by the year 2025.
Advances in Computing Power: The availability of powerful GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) and cloud computing platforms has made it easier and more cost-effective to train machine learning models on large datasets.
Improvement in Algorithms: The development of new algorithms, such as deep learning techniques, has significantly improved the accuracy and performance of machine learning models.
Increased Investment: Companies and governments are investing heavily in machine learning research and development, which has led to rapid advancements in the field.
Applications in Various Industries: Today majority of the businesses, companies, and industries, dealing with a huge amount of data have adopted machine learning methods to evaluate customers' trends, behaviour, and business patterns which have helped them in understanding the needs and demands of the customer in a better way, increasing customer retention, improving customer service, adopting a better and improved marketing strategy. This has made them gain a competitive edge over others and function more efficiently and effectively.
The Incredible Impact of Machine Learning Across Various Sectors
Financial Sector: Machine learning has huge applications in this sector as it can solve much more complex and technical problems such as fraud detection, customer data management, algorithmic stock trading, identifying investment opportunities, securing payment transfers, financial monitoring, providing financial advisory, etc.
Healthcare: This sector also has a massive demand for Machine Learning, from studying the data and identifying trends and behaviour which help in the identification and treatment of chronic diseases. We can soon expect several machine learning-based applications that will play a vital role in analyzing a patient’s health in real time. Other applications in healthcare are in the discovery and manufacturing of drugs, clinical trials and research, smart health records, Outbreak prediction, etc.
Transportation: Supply chain and logistics operations have benefited significantly from the increase in the popularity of machine learning. With its capability of evaluating the input dataset as well as identifying the trends, Machine learning finds huge applications in the transportation sector such as in self-drive cars, finding and making the most efficient and safe routes, collection of traffic data, and other public transportation services, etc.
Manufacturing Industries: Machine learning performs tasks such as human resource management, controlling warehouses, demand forecasting, optimization of the supply chain and transportation, prediction of machine breakdown or malfunction, minimizing the shipping and delivery cost and time, etc.
Government: Machine learning is used by various government authorities as they have numerous information resources, that must be analyzed to get insights. It holds a massive amount of applications in policymaking, planning, and providing services to citizens. Tasks that do not require a high amount of authorization such as the generation of bills, automated payment system, routing the complaints and queries of the people to proper authority, and answering them are done by machine learning. Machine learning also plays a huge role in preventing crime by analyzing the huge surveillance data for threats in real-time. Law-enforcing bodies use machine learning and AI (Artificial Intelligence) to track missing criminals with the help of voice and image recognition techniques.
E-Commerce and Retail: E-commerce and retail sectors have greatly benefited from the use of machine learning and have a huge number of applications for it. Several e-commerce websites such as Amazon, Flipkart, Walmart, etc. are using machine learning to analyze data, understand the trends and behaviour of the customer, and improve the customer experience by providing a personalized shopping experience. Machine learning has helped these e-commerce websites in designing website and product recommendation systems, implementing dynamic pricing, using smart chat-bots to enhance and improve customer service, etc.
A Look at the Different Types of Machine Learning Algorithms
Supervised Learning: This type of machine learning is used when the data is labelled and the model needs to learn from it. The algorithm is trained on a labelled dataset, where each input data has a corresponding output. The model learns to make predictions based on the input data by identifying patterns and relationships in the training data.
Unsupervised Learning: This type of machine learning is used when the data is not labelled and the model needs to identify patterns or relationships on its own. The algorithm is given an unstructured dataset and is expected to identify patterns or relationships without any pre-existing knowledge of what to look for.
Semi-supervised Learning: This type of machine learning is a combination of both supervised and unsupervised learning. The algorithm is given a partially labelled dataset, where some of the input data has corresponding output labels, and some do not. The model learns from the labelled data to make predictions on the unlabeled data.
Reinforcement Learning: This type of machine learning involves training a model to make decisions in an environment. The model interacts with the environment and receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties based on its decisions. The model learns to make better decisions by maximizing its rewards over time.
Creating Your First Machine Learning Model Using the IRIS Dataset
In this section, we will explore the process of creating your first machine-learning model using the IRIS dataset. The IRIS dataset is a classic dataset used in machine learning to classify different species of the Iris flower.
Brief Description of the Dataset
The IRIS dataset consists of 150 samples of iris flowers. Each sample contains four features: sepal length, sepal width, petal length, and petal width. The samples belong to one of three classes: Iris setosa, Iris versicolor, and Iris virginica. Our task is to train a model that can predict the class of a given sample based on its four features.
Building the Machine Learning Model with Python
In this section, we will dive into the exciting world of machine learning by building our first ML model using Python. By following the step-by-step process outlined below, you will learn how to train a machine learning model using the popular Iris dataset.
Step 1: Importing the Required Libraries To begin, we need to import the libraries that we will use for our analysis. We will be using pandas, numpy, matplotlib, seaborn, and scikit-learn libraries.
#Importing the libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
Step 2: Reading the Dataset: Next, we will read the dataset from the UCI Machine Learning Repository using the pandas library. We will also give names to the columns using the 'names' parameter.
#defining the features
features = ["sepal_length", "sepal_width","petal_length", "petal_width", "target_class"]
df = pd.read_csv("<http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/iris/iris.data>", names = features) #reading the dataset
Step 3: Exploring the Dataset Before we start building our model, we need to explore the dataset to understand its structure and properties.
We can start by checking the shape of the dataset using the shape attribute.
df.shape
This will return (150, 5), indicating that there are 150 rows and 5 columns in the dataset.
We can then display the first five rows of the dataset using the head() method.
df.head()
This will display the first five rows of the dataset as shown below.
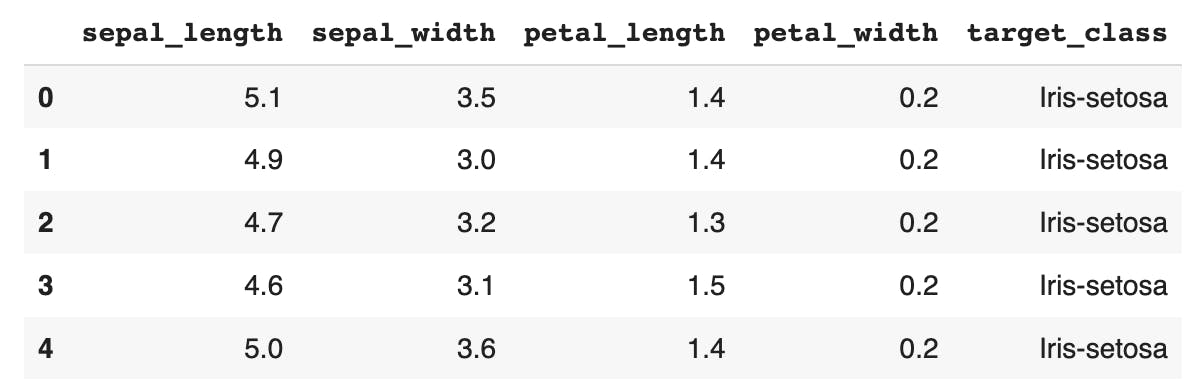
We can also display information about the dataset using the info() method.
df.info()
This will display the column names, data types and other information as displayed below.
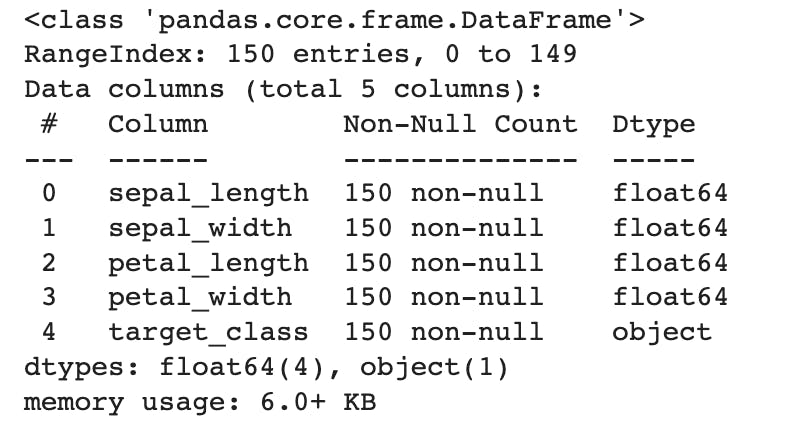
Next, we need to check if there are any missing values in the dataset. We can use the isnull() method to check for missing values, and the sum() method to count the number of missing values.
df.isnull().sum()
Since the output shows zero for all the columns, there are no missing values in the dataset.
We can also analyze the dataset using the describe() method.
df.describe()
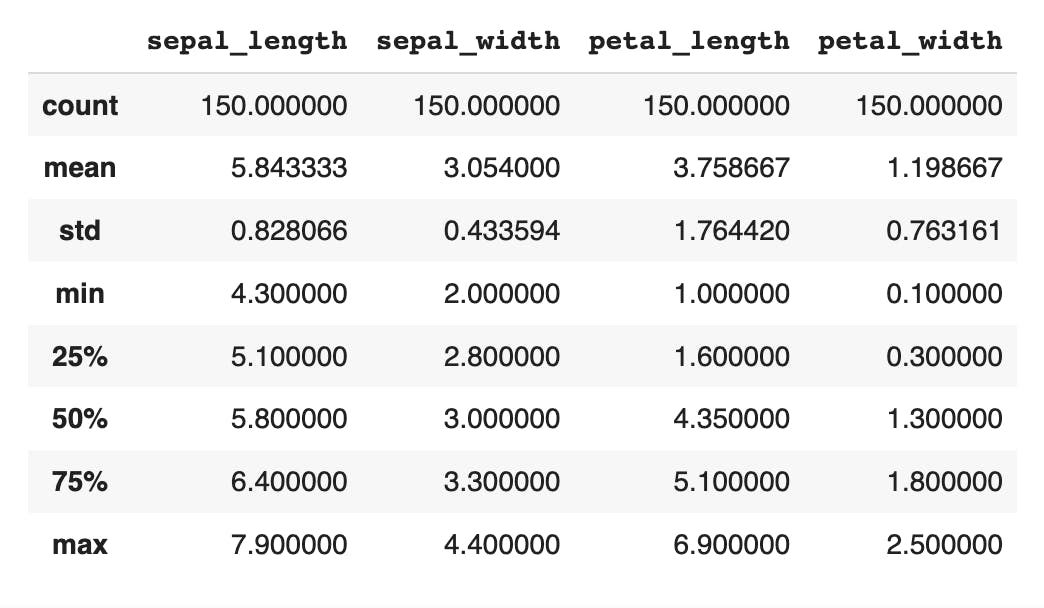
This will display some statistics about the dataset, such as the mean, standard deviation, and quartiles of each feature.
Step 4: Visualizing the Dataset Visualizing the dataset can help us gain insights into the data and identify any patterns or relationships between the features.
We can start by creating a pair plot using the seaborn library.
sns.pairplot(df, hue = 'target_class')
This will create a pair plot of all the features with the hue parameter set to the target class.
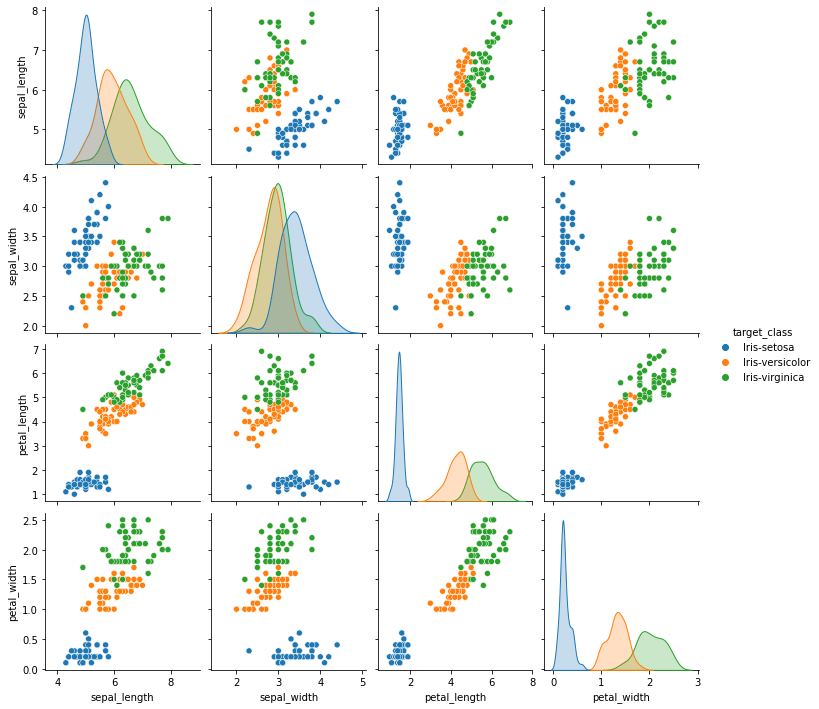
From the pair plot, we can make the following observations:
iris-setosa is well separated from the other two flowers, while iris-virginica and iris-versicolor have some overlap.
Additionally, we can see that iris-virginica is the longest flower, while iris-setosa is the shortest flower.
Next, we can analyze the distribution of the target class in our dataset. We can do this by counting the number of entries for each species in the dataset and plotting the result using a pie chart.
TargetClass = {}
TargetClass["Iris-setosa"] = (df["target_class"] == 'Iris-setosa').sum()
TargetClass["Iris-versicolor"] = (df["target_class"] == 'Iris-versicolor').sum()
TargetClass["Iris-virginica"] = (df["target_class"] == 'Iris-virginica').sum()
print(TargetClass)
#Visualising the above findings using a pie chart.
labels = []
count = []
for x, y in TargetClass.items():
labels.append(x)
count.append(y)
plt.figure(figsize = (8, 8))
plt.pie(count, labels=labels,autopct='%1.2f%%')
plt.title('Pie chart showing Target Class Distribution')
plt.show()
Here, we first create a dictionary called TargetClass and count the number of entries for each species using the .sum() function. We then use this dictionary to create a pie chart of the target class distribution.
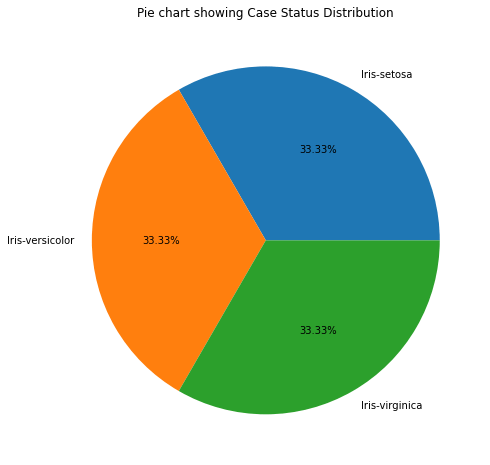
We can see that each species has an equal number of entries in the dataset.
Step 4: Splitting the dataset into training and testing sets
Next, we will separate the features and target class, and split the dataset into training and test datasets.
#Separating the features and the target class
X = df.drop('target_class', axis = 1)
Y = df['target_class']
#Splitting the dataset into training and test datasets in the ratio 80:20.
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2 ,random_state = 105 )
Y_train.value_counts()
Here, we separate the features and target class into X and Y respectively. We then use the train_test_split() function from scikit-learn to split the dataset into training and test datasets in the ratio 80:20. We also set the random state to 105 to ensure the same split is generated every time the code is run.
Finally, we can train a logistic regression model on the training dataset and evaluate its accuracy using the test dataset.
We create a logistic regression model using the LogisticRegression() function from scikit-learn, and fit it to the training dataset using the fit() function. We then use the predict() function to predict the target class for the test dataset, and evaluate the accuracy of the model using the accuracy_score() function.
#Training the Logistic Regression Model on the training dataset
LR = LogisticRegression()
LR.fit(X_train, Y_train)
Y_pred = LR.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(Y_test, Y_pred)
print(accuracy*100,'%')
We also plot a confusion matrix using the confusion_matrix() function from scikit-learn, and visualize it using a heatmap from seaborn.
#plotting the classification matrix
plt.figure(figsize = (6, 6))
CM = confusion_matrix(Y_test, Y_pred)
sns.heatmap(CM,annot=True)
plt.xlabel('Predicted Label')
plt.ylabel('Actual Label')
plt.show()
#printing the classification report.
print(classification_report(Y_test, Y_pred))

Finally, we print a classification report using the classification_report() function from scikit-learn.

Conclusion
In conclusion, Machine Learning is a rapidly growing and promising field that has the potential to transform various sectors and revolutionize the way we live, work, and interact with technology. This blog provided an introduction to Machine Learning, its brief history, and the different types of algorithms used in it. We also learned how to create our first ML model using the IRIS dataset and gained practical insights into the concepts we learned. I hope this blog has helped provide insight into the world of Machine Learning.
For further reference, I have attached the code file to this blog. You can download it from the link provided below.
Link to code file: Iris Flower Classification using Machine Learning
Don't forget to follow the blog for more informative articles on Machine Learning, Data Science, and other trending topics in the world of technology. Thank you for reading!