Understanding the Fundamentals of RESTful API Architecture
Get an in-depth look at the key concepts and principles of RESTful API design.
Introduction
Welcome to the exciting world of REST APIs! If you're new to this term, REST stands for Representational State Transfer, which is a software architectural style that allows for communication between two different systems over the internet. To give you an idea of how REST APIs are used in the real world, let's take a look at some examples. If you've ever used an online shopping platform, such as Amazon or Flipkart, you've interacted with REST APIs. These platforms use REST APIs to enable users to search for products, add them to their shopping cart, and complete their purchases. Similarly, social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter rely heavily on REST APIs to enable users to post updates, share content, and interact with other users. In simpler terms, it enables different software applications to talk to each other and exchange data.
The concept of REST APIs first emerged in the early 2000s when Roy Fielding introduced it in his doctoral dissertation. Since then, REST has evolved significantly and become the go-to approach for building web services. Today, REST APIs are used in a wide range of applications, from mobile apps to e-commerce websites, social media platforms, and more.
In this blog, we'll explore the ins and outs of REST APIs, including their architecture, methods, and best practices. We'll also take a look at some real-world use cases and explore how REST APIs are shaping the future of software development**.**
REST API Fundamentals
REST APIs are built around the concept of resources and representations. In REST, a resource can be anything that is of interest to the client, such as a customer, a product, or a blog post. Each resource is identified by a unique identifier, known as a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI).
Representations, on the other hand, are the different ways in which a resource can be presented. For example, a customer resource can be represented as a JSON object or an XML document. Similarly, a product resource can be represented as an image, a video, or a text description.
HTTP methods and status codes are the building blocks of REST APIs. HTTP methods are used to perform different operations, also known as CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations on a resource. The most commonly used HTTP methods in REST APIs are GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE.
The POST method: It is used to create a new resource on the server. For example, when a client sends a POST request to the URI of a customer resource, the server creates a new customer resource based on the data provided in the request.
The GET method: It is used to retrieve a resource from the server. For example, when a client sends a GET request to the URI of a customer resource, the server responds with the representation of that resource.
The PUT method: It is used to update an existing resource on the server. For example, when a client sends a PUT request to the URI of a customer resource, the server updates that resource with the data provided in the request.
The PATCH method: It is used to update a part of an existing resource on the server. For example, when a client sends a PATCH request to the URI of a customer resource, the server updates only the fields specified in the request.
The DELETE method: It is used to delete a resource from the server. For example, when a client sends a DELETE request to the URI of a customer resource, the server deletes that resource from its database.
HTTP status codes are used to communicate the status of a request to the client in REST APIs. The most commonly used HTTP status codes are 200 OK, 201 Created, 204 No Content, 400 Bad Request, 401 Unauthorized, 404 Not Found, and 500 Internal Server Error. These codes convey information about the success or failure of a request, which can help developers diagnose and fix issues.
RESTful web services are web services that follow the principles of REST. They expose a set of resources over HTTP, and clients interact with these resources using HTTP methods and representations. RESTful web services are easy to build, maintain, and scale, which makes them a popular choice for building web applications. With their simple and standardized approach to resource management, RESTful web services have become a cornerstone of modern web development.
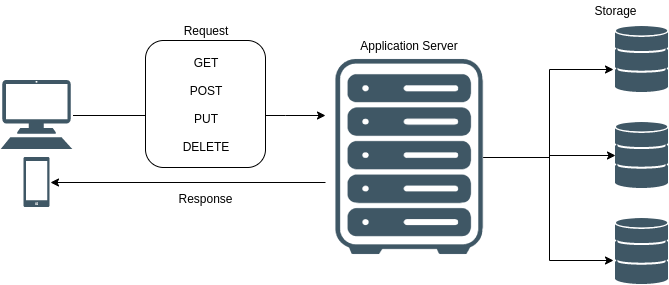
In conclusion, understanding the fundamentals of resources and representations, HTTP methods and status codes, and RESTful web services is essential for building and consuming REST APIs. By following these principles, developers can build scalable, flexible, and reliable web applications that can communicate seamlessly with other systems over the internet.
Characteristics of a RESTful API
One of the biggest advantages of REST APIs is that they are platform-independent, which means that they can be used with any programming language, operating system, or device. Additionally, REST APIs are lightweight and scalable, making them perfect for building microservices and other distributed systems. RESTful APIs have gained popularity over the years due to their simplicity and flexibility. A well-designed RESTful API is characterized by the following key features:
Stateless Architecture: RESTful APIs do not maintain any state on the server between requests. This means that each request is independent of any other request, and the server does not need to keep track of any session or context information. This makes RESTful APIs scalable and easy to maintain.
Cacheable Responses: RESTful APIs should be designed to provide cacheable responses whenever possible. This means that the server should include cache-control headers in the response to allow clients to cache the response and avoid making unnecessary requests to the server.
Uniform Interface: RESTful APIs should have a uniform interface that defines how clients can interact with the resources. The interface should be consistent across all resources, and it should be easy to understand and use. The interface should also be independent of the implementation details of the server, making it easier to evolve and change over time.
Layered System: RESTful APIs should be designed as a layered system, where each layer is responsible for a specific set of functions. This allows for better separation of concerns and makes it easier to maintain and evolve the system over time.
Client-Server Architecture: RESTful APIs should follow a client-server architecture, where the client and server are separate entities. This allows for better separation of concerns, and it makes it easier to scale the system by adding more servers as needed.
In summary, a well-designed RESTful API should have a stateless architecture, provide cacheable responses, have a uniform interface, be designed as a layered system, and follow a client-server architecture. By following these principles, developers can build scalable and maintainable APIs that can evolve and adapt to changing requirements over time.
Popular Frameworks for Developing RESTful APIs
There are several popular frameworks and libraries available for implementing RESTful APIs. Some of the most commonly used ones are:
Express.js: Express.js is a popular Node.js framework for building web applications and RESTful APIs. It provides a simple and flexible API for handling HTTP requests and responses, making it an excellent choice for building RESTful APIs.
Django REST framework: Django REST framework is a powerful and flexible toolkit for building Web APIs with Django. It provides a range of tools and libraries for building RESTful APIs quickly and easily.
Flask: Flask is a lightweight and flexible Python web framework for building web applications and RESTful APIs. It provides a simple and easy-to-use API for handling HTTP requests and responses.
Ruby on Rails: Ruby on Rails is a popular web application framework that can also be used to build RESTful APIs. It provides a range of tools and libraries for building APIs quickly and easily.
There are several other popular frameworks that developers can use to write RESTful APIs, such as Spring Boot for Java, ASP.NET for C#, and Laravel for PHP. Spring Boot is a popular framework for building enterprise-level applications with its vast library of modules and plugins. Similarly, ASP.NET is widely used for building APIs on the Microsoft platform and offers a range of features for developing secure and scalable APIs. Laravel is an excellent choice for PHP developers, as it provides a clean and intuitive syntax, as well as robust routing and middleware capabilities. There are also many other frameworks available, each with its own set of strengths and weaknesses, so one should consider their specific needs and choose a framework that suits their project requirements.
Conclusion and Future Scope
In conclusion, RESTful APIs have become a crucial part of modern web development due to their simplicity, scalability, and flexibility. By following the key principles of a RESTful API, developers can build APIs that are easy to understand, use, and maintain.
To recap, the key characteristics of a well-designed RESTful API include stateless architecture, cacheable responses, a uniform interface, a layered system, and a client-server architecture. Best practices for designing a RESTful API include using descriptive URIs, using HTTP methods correctly, using HTTP status codes, using plural nouns, and versioning.
The future of RESTful APIs is promising, with increasing demand and importance for modern web application development. As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, REST APIs will become even more crucial for enabling seamless communication between different systems and applications. We can expect to see more innovations in API design, security, and management as the demand for APIs increases. Furthermore, REST APIs will continue to play a vital role in the development of modern web applications, and developers who master RESTful API design will be well-positioned to succeed in the future of web development. In the future, we can also expect to see more sophisticated REST APIs that leverage emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling businesses to build more intelligent and efficient systems that can automatically respond to changing conditions and make data-driven decisions. All in all, the future of REST APIs is exciting and holds immense potential and developers who master RESTful API design will be well-positioned to succeed in the future of web development.
I hope this article has given you a better understanding of REST APIs and how they work. If you have any questions or suggestions, feel free to leave a comment below. Don't forget to like and share this article if you found it helpful. And if you're new to the world of APIs, make sure to check out my previous blog which covers the basics of APIs and how they work. Thanks for reading!